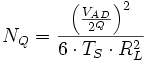Quantization noise: Difference between revisions
(uploaded equation. Gives users a simple and effective way to calculate quant noise.) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
During the [[quantization]] process some precision gets lost, this changes the signal somewhat, the difference between the original signal and the quantized signal is called quantization noise or the (rounding error). It is commonly expressed by the root-mean-square error equation in | During the [[quantization]] process some precision gets lost, this changes the signal somewhat, the difference between the original signal and the quantized signal is called quantization noise or the (rounding error). It is commonly expressed by the root-mean-square error equation in engineering. | ||
Revision as of 18:09, 21 June 2005
During the quantization process some precision gets lost, this changes the signal somewhat, the difference between the original signal and the quantized signal is called quantization noise or the (rounding error). It is commonly expressed by the root-mean-square error equation in engineering.
Q is the resolution or the amount of bits in the converter.
V_AD is the analog voltage range of converter expressed in (Volts)
T_S is the sampling interval of the converter expressed in (Seconds)
R_L^2 is resistance of the converter expressed in (Ohms).